2020 Nature Human Behaviour, Addressing the digital skills gap for future education
2020 Nature Human Behaviour, Addressing the digital skills gap for future education
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused rushed digitalization of primary and secondary (K12) student education, and cyber-risks such as bullying, technology addiction, and misinformation must be addressed. There is an urgent need to coordinate global efforts for digital skills education and training, which can help students succeed in the digital age while curbing risks and inequality.
Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41562-021-01074-z
2019 Global Standards Report
For the world to build comprehensive digital competencies with speed, scalability, and sustainability, there is an urgent need for effective coordination and consensus towards building a common framework with a set of definitions, structure, and taxonomy. In this report, we present the DQ Framework as the solution. Read more here: https://www.dqinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/DQGlobalStandardsReport2019.pdf
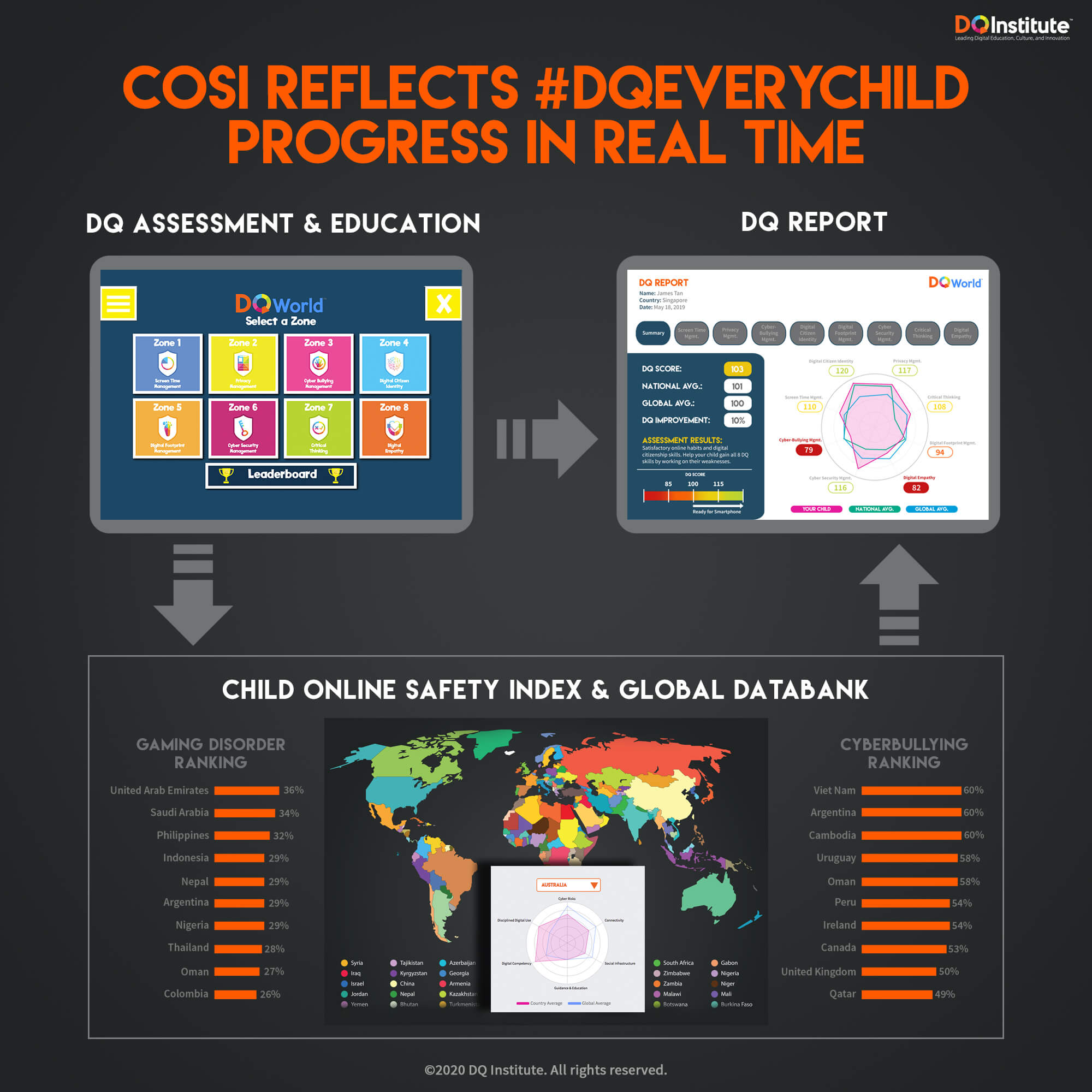
2018 Global DQ Impact Report
On Safer Internet Day (6th February 2018), the 2018 DQ Impact Report was published in association with the World Economic Forum. As part of our #DQEveryChild movement to empower children with digital intelligence (DQ), the multinational report delved into the current state of online safety and digital citizenship among 38,000 8-12 year olds across 29 countries. In particular, we focused on how children became exposed to cyber-risks and how these risks may affect them.
Our key finding, that 56% of 8-12 year olds are exposed to at least one cyber-risk (including risks like cyberbullying and online grooming), is particularly revealing of the work that lies ahead for all of us in the creation of an ethical digital ecosystem for this generation of digital natives.
The full report and more information can be found below:
2018 Nature Outlook
This article published in Nature Outlook on October 2018 outlines how DQ can help address the need for digital intelligence.
Resources
2017 Efficacy of the Help-Reporting System
In the 2016 DQ Pilot Impact Study, about 60% of children who were exposed to cyber-victimization wanted extra help to handle their cyber issues. A 2015 DQ e-counselling study conducted by the National Institute of Education, Singapore also revealed that timely intervention is critical to improve emotional well-being of children who are exposed to cyber-risks.
From September 2017, DQWorld.netTM will include a unique help-reporting system to detect a child’s exposure to various cyber-risks and provide opportunities to proactively intervene to help at-risk child.
The study will be conducted to understand its effectiveness through Private-Public Partnership in Singapore and Australia:
• Singapore: Singtel (private) – National Council of Social Service (public) – TOUCH Cyber Wellness, Feiyue (civil society)
• Australia: via Optus (Singtel) and Kids Helpline Strategic Corporate Partnership – collaboration and knowledge sharing
Resources
Online Counselling DQ Studies
A 2017 DQ online counselling study conducted by the National Institute of Education (NIE), Singapore revealed that lack of nonverbal cues enhanced children’s psychological safety and willingness to self-disclose online. TCPs also found it helpful to use a solution-focused approach to work with children and to adapt their face-to-face counselling techniques to online counselling through the use of SITCOMS (Skills in Text-based Communication).
Find the study here: https://doi.org/10.18401/2017.7.2.3
A 2018 DQ e-counselling study also conducted by NIE revealed that online counselling helped children find solutions as well as support for their emotional and practical needs.
Find the study here: https://doi.org/10.1080/03069885.2018.1485871
Resources
DQ World Methodology
DQ World is an innovative research-based, e-learning platform that is specifically designed for young users of digital media and technology. The online educational platform has been recognized by two UNESCO awards for its pioneering efforts to promote digital citizenship education among children. DQ World’s approach is pioneering in the sense that it has transformed how nations approach digital education. Indeed, more and more school programs are incorporating technology in a variety of ways: some use computers in the classroom, some make online assistance available to children, and some teach coding and even robotics.
Basic digital citizenship skills, however, are often overlooked by educators and parents despite being fundamental to a person’s ability to get the most out of technology and to avoid risks. One reason for this gap is that teachers themselves have not been trained in the area of digital citizenship education, and they are already over-burdened with other teaching needs and requirements. Therefore, any comprehensive program needs to either (1) include training for teachers and fit in within the curriculum, or (2) provide training directly to students with only basic support needed from teachers. DQ World is based on this second approach, and is a compatible with a wide variety of learning environments.
Resources